Fuel Your Body with the Right Balance: Mastering Macronutrients for Optimal Health
Macronutrients are the essential building blocks of your diet: protein, fats, and carbohydrates. These three components not only provide the energy your body needs to function but also play distinct roles in supporting muscle growth, hormone production, and overall well-being. Whether your goal is to build muscle, lose weight, or maintain your energy throughout the day, understanding how to balance your macronutrients is a game-changer for your health and fitness journey.
What Are Macronutrients?
Macronutrients are nutrients required in large amounts to provide energy and support the body’s vital functions. Unlike micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), macronutrients directly contribute to your caloric intake and are the fuel that powers your body.

The Three Macronutrients:
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair, growth, and immune system support.
- Fats: Necessary for hormone production, brain health, and cellular function.
- Carbohydrates: The body’s primary energy source, fueling your brain and physical activities.
How They Work Together:
Your body relies on a combination of these macronutrients to function optimally. Each macronutrient has a unique role, and finding the right balance tailored to your needs can significantly improve your health outcomes.
Why Macronutrient Balance Matters
Achieving the right balance of macronutrients is critical for optimal health. While the “perfect” ratio varies depending on individual goals, understanding how each macronutrient impacts your body is the first step toward creating a diet that works for you.

Benefits of Macronutrient Balance:
- Supports Your Goals: Whether you aim to gain muscle, lose weight, or increase endurance, adjusting your macronutrient intake can help achieve those goals.
- Enhances Energy Levels: A well-balanced diet prevents energy crashes and sustains performance throughout the day.
- Improves Recovery: Proper nutrition helps your body repair and recover after workouts.
- Promotes Longevity: Balancing macronutrients reduces the risk of chronic diseases and supports overall health.
The Science of Macronutrient Ratios
Understanding the science behind macronutrient ratios is crucial for creating a diet tailored to your needs. While no one-size-fits-all approach exists, here are common ratios and how they align with different goals:

1. Weight Loss:
- Higher Protein, Moderate Fats, Lower Carbs
- Example Ratio: 40% Protein, 30% Fats, 30% Carbs
- Why It Works: Protein boosts satiety and preserves muscle during calorie deficits.
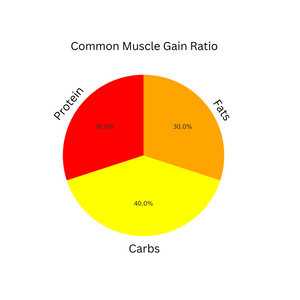
2. Muscle Gain:
- Higher Protein, Higher Carbs, Moderate Fats
- Example Ratio: 40% Carbs, 30% Protein, 30% Fats
- Why It Works: Carbs fuel workouts, while protein supports muscle repair.

3. Endurance Training:
- Higher Carbs, Moderate Protein, Lower Fats
- Example Ratio: 50% Carbs, 30% Protein, 20% Fats
- Why It Works: Carbs are the primary energy source for long-duration activities.
Breaking Down Each Macronutrient

Protein: The Building Block
Protein is essential for muscle growth, immune health, and enzymatic functions. Unlike fats and carbohydrates, protein cannot be stored in the body, so consistent intake is vital.
Example Sources: Chicken breast, turkey, salmon, tuna, tofu, tempeh, eggs, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, lentils, black beans, edamame.
Daily Needs: Aim for 0.8–1.2 grams of protein per pound of body weight, depending on activity level.

Fats: The Hormonal Powerhouse
Healthy fats are critical for brain function, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. While fats are calorie-dense, they’re essential for a balanced diet.
Example Sources: Avocados, almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds, olive oil, coconut oil, fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel, sardines), dark chocolate (85% or higher cocoa content), full-fat dairy (e.g., cheese, butter), pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds.
Daily Needs: Fats should comprise 20–35% of your daily calorie intake.

Carbohydrates: The Energy Source
Carbs are the body’s go-to energy source, particularly during high-intensity activities. Choosing the right carbs—complex over simple—is key to sustained energy.
Sources: Sweet potatoes, quinoa, oats, brown rice, whole wheat bread, chickpeas, lentils, apples, bananas, spinach, broccoli, berries (e.g., blueberries, raspberries, blackberries).
Daily Needs: Carbs should make up 30–50% of your daily calorie intake, depending on activity level.
Common Myths About Macronutrients
Myth 1: Carbs Make You Fat
- Fact: Excess calories, not carbs, lead to weight gain. Complex carbs provide sustained energy and are crucial for active lifestyles.
Myth 2: All Fats Are Bad
- Fact: Healthy fats, such as omega-3s, support brain health and reduce inflammation. Avoid trans fats and focus on unsaturated fats.
Myth 3: You Need High Protein to Build Muscle
- Fact: While protein is essential, consuming more than your body needs does not yield extra benefits. Balance is key.
Explore More on Your Health Journey
Dive deeper into topics that inspire and empower your wellness journey. From expert health tips to actionable fitness advice, our blog is packed with valuable insights to help you become the best version of yourself. Start exploring today and take your first step toward lifelong health!

Feb 12, 2025
Can You Really Speed Up Your Metabolism? The Truth Behind Fat Loss and Energy Burn
Read more
How Can You Optimize Sleep, Learning, and Metabolism Using Science?
Read more
Are You Drinking Water Wrong? The Science of Hydration, Electrolytes, and Water Quality You Need to Know!
Read more
Are You Counting Your Macros WRONG? The Science You Need to Know!
Read more
The Science of Stretching: Unlocking Flexibility for Strength, Longevity, and Mental Resilience
Read more

Feb 4, 2025
The Science of Weight, Longevity & Social Media: What I Wish I Knew Sooner
Read more






